Do you want to discover everything there is to know about food 3D printing? At Imprimy, we are ready to answer all the questions you may have.
Food 3D printing is a specific form of 3D printing that allows for the production of food.
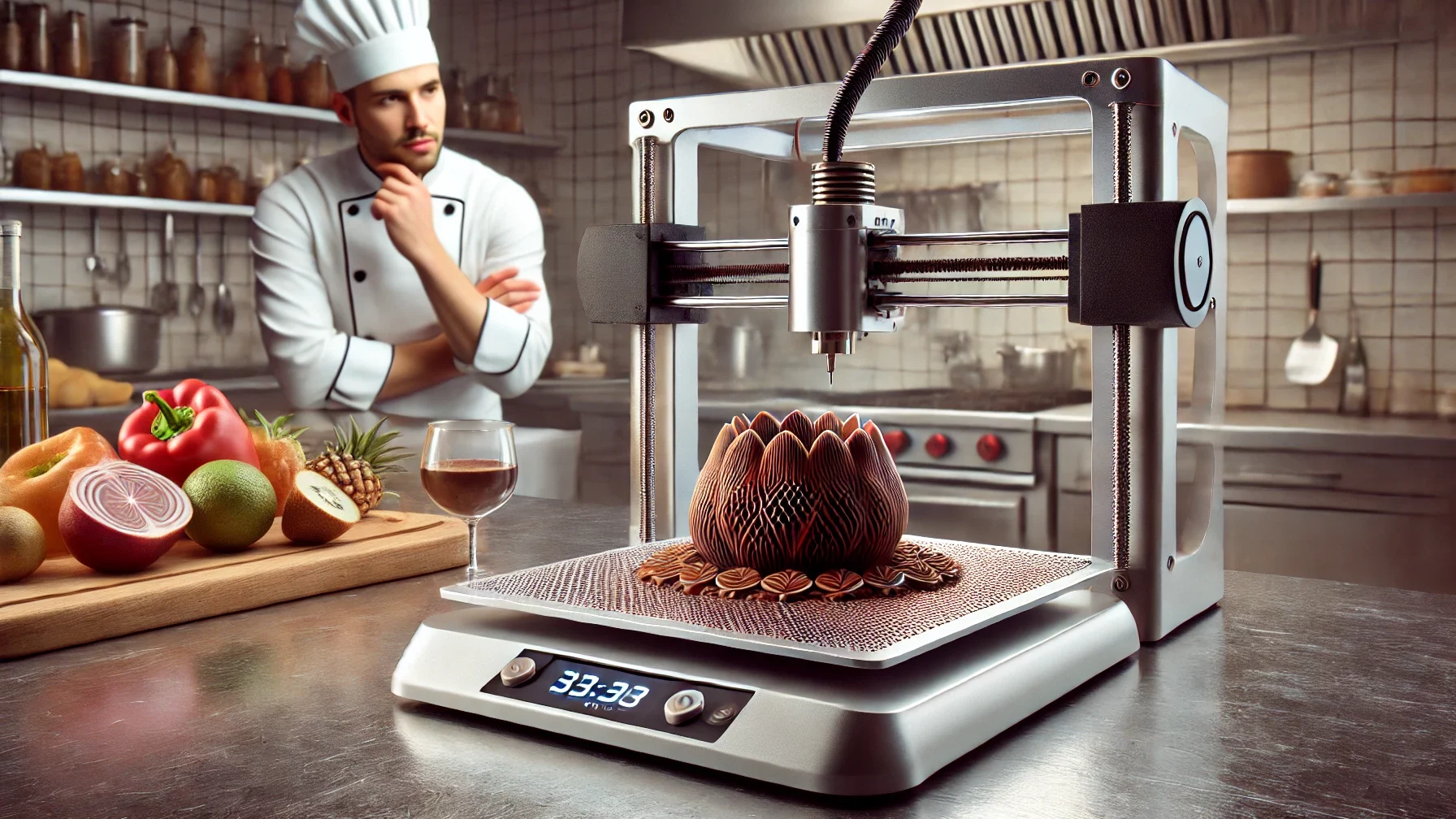

What is 3D food printing?
Thanks to 3D food printing, you can produce edible products for humans or animals by successively layering different materials.
The basic principle of 3D food printing
The basic principle of 3D food printing is the same as in traditional additive manufacturing. The 3D printer specifically designed to produce food will stack numerous successive layers of edible materials. This layering process results in a 3D-printed food item.
Before starting production, you must first create a digital model of the food you wish to produce. This can be done using 3D modeling software.
Once your model is ready, you can send it to your 3D food printer. This type of printer uses ingredients like purees, doughs, chocolate, or even plant-based proteins instead of traditional filaments or resin.
3D food printing offers vast customization possibilities, both in shape and texture. This allows you to explore new creative avenues by producing original meals or unique food decorations.
The different technologies used in 3D food printing
The technologies used in 3D food printing vary depending on the type of ingredients you want to use and the results you are aiming for.
The main technology used in 3D food printing is extrusion, similar to FDM technology. Your 3D food printer will melt or heat edible materials before extruding them layer by layer. At the end of the process, you will obtain the object you modeled, created with the edible material used by your printer.
Materials compatible with 3D food printing
3D food printing uses a wide variety of edible materials, allowing you to create food objects with diverse textures and flavors. Among the most commonly used materials are:
- More innovative materials, like plant-based proteins or insect-based ingredients, are beginning to be used in 3D food printing to address ecological and nutritional concerns.
- Pastes and purees made from potatoes, vegetables, or fruits, which can be extruded from individual refill cartridges to form complex structures.
- Chocolate is also very popular due to its ability to melt and solidify quickly, making it ideal for creating decorations or sculptures.
- Gels, such as algae gels or yogurt gels, and sugar pastes are used for fine and precise printing, especially in pastry making.
What are the advantages of 3D food printing?
3D printing of food offers you many advantages, such as enhanced customization, optimization of ingredients to reduce waste, as well as increased innovation and accessibility for certain specialized foods.
Customization of 3D Food Printing
Thanks to 3D food printing, you can customize meals or snacks as you wish. This customization can be based on your preferences and specific dietary needs.
With 3D food printing, you can adjust not only the shape, but also the texture, flavors, and even the nutritional composition of the foods you consume.
You can print cake decorations, chocolate sculptures, or dishes shaped like unique characters. This technology offers a personalized culinary experience, which can be especially appealing during special events like birthdays or weddings.
Moreover, 3D printing allows you to adapt your meals to your specific nutritional requirements, particularly if you follow:
- A gluten-free diet,
- A vegetarian diet,
- A low-calorie diet.
Indeed, the customization offered by 3D food printing goes beyond aesthetics. It provides tailor-made solutions that help you navigate your dietary restrictions, specific tastes, or even certain medical requirements.
Optimization of Ingredients Used in 3D Food Printing
The ingredients used in 3D food printing are specifically developed and prepared for this precise application.
3D food printing allows you to better manage quantities of ingredients, thus reducing food waste during your cooking sessions. Additionally, your ingredients are used more accurately, especially in terms of the amounts used. This helps avoid producing excess, which often happens during traditional cooking.
Moreover, 3D food printing enables more homogeneous mixing of different materials than if done manually. This type of mixing promotes better integration of flavors and textures in the final product.
3D food printing also paves the way for more sustainable food production by allowing the use of alternative ingredients such as plant-based proteins or algae, which can be printed as innovative food substitutes.
The optimization of ingredients in 3D food printing also extends to recipe customization, where users can adjust ingredients according to their specific nutritional needs.
Finally, the ability to create foods with a more precise structure allows better control over their preservation and shelf life, contributing to more efficient resource management and further waste reduction.
Culinary Innovation Enabled by 3D Food Printing
3D food printing opens up exciting new perspectives in culinary innovation. If you are a professional chef, you can push the traditional boundaries of your craft.
Using this technology, you can design new shapes and textures, combine ingredients in original ways, or create personalized dishes based on the flavors you want or specific nutritional needs you wish to address.
If you are a pastry chef, you can print complex food structures, such as sugar sculptures or chocolate decorations, with a precision and fineness impossible to achieve manually. These 3D printed edible elements can decorate your creations.
3D food printing also allows you to explore concepts like multi-layered food production, where each layer offers the consumer a different texture or flavor, creating unique tasting experiences.
Accessibility and Nutrition of 3D Food Printing
3D food printing has the potential to play a significant role in food accessibility and nutrition. Indeed, this technology can offer personalized solutions to meet specific dietary needs while producing balanced meals.
From a nutritional perspective, 3D printing allows the creation of dishes perfectly adapted to consumers’ dietary requirements by adjusting ingredients to meet specific criteria such as:
- Protein intake,
- Vitamin intake,
- Special diets.
All these possibilities enable you to offer healthier food tailored to individual needs, such as those of:
- Elderly people,
- Patients with eating disorders,
- Athletes requiring specific nutritional intake.
On the accessibility side, although the most advanced 3D food printers remain relatively expensive, their rapid development has led to more affordable models that can be integrated into homes or institutions such as schools or hospitals.
Finally, this technology can contribute to reducing food waste by allowing more precise management of ingredients and portions used in your cooking recipes.
What are the concrete applications of 3D food printing?
Currently, 3D food printing is mainly used in specific sectors such as the gastronomic industry, pastry making, and in the context of innovations.
3D Food Printing in the Gastronomic Industry
3D food printing is starting to make its mark in the gastronomic industry thanks to the new creative possibilities it offers and its unprecedented precision. Machines in high-end restaurants allow chefs to create unique presentations that would be difficult or even impossible to make by hand.
3D food printing also enables them to customize meals according to their customers’ preferences, adapting the shapes, flavors, and nutritional elements. This technology thus provides a personalized and innovative culinary experience for customers in restaurants equipped with these machines.
Some chefs also use 3D printing to explore experimental culinary concepts, such as creating dishes with unexpected textures, transforming the sensory experience of diners.
Moreover, in large-scale production, 3D food printing allows for better resource management and cost reduction.
Finally, 3D food printing opens up unprecedented sustainability potential in the food industry by enabling the creation of foods from plant proteins or alternative ingredients, addressing environmental concerns.
3D Food Printing in Pastry Making
3D printing is revolutionizing the pastry sector by allowing the production of complex decorations and designs. You can create true edible works of art with unmatched precision and detail.
With edible 3D printing, you can easily make sugar sculptures, chocolate flowers, or custom patterns on cakes, candies, or desserts. It also enables exploration of new textures and unique flavor combinations by layering different ingredients in innovative ways.
Additionally, this technology helps optimize pastry production by reducing ingredient waste and facilitating the creation of products in large quantities, while maintaining consistent quality.
3D food printing also allows for personalized creations tailored to special events, such as wedding cakes or custom desserts for specific diets.
3D Printing in the Food of Tomorrow
3D printing could become an integral part of the food of tomorrow, offering exciting development prospects, especially in terms of sustainability, customization, and culinary innovation.
This technology has the potential to play a key role in creating meals tailored to specific nutritional needs, whether for the elderly, astronauts, or food solutions for crisis regions.
By using alternative ingredients such as plant proteins or insects, 3D food printers can also address environmental challenges by producing meals that are both healthy and sustainable, while reducing food waste.
Additionally, edible 3D printing would allow for more efficient food production, optimizing the amount of ingredients required and minimizing waste.
The integration of 3D printing into food production could also promote greater accessibility to balanced meals by facilitating large-scale production while maintaining high quality standards.
Experimental Projects in 3D Food Printing
3D food printing fits perfectly into experimental projects as it offers innovative horizons and paves the way for practical and creative applications in various fields.
Some projects experiment with using 3D printing to create personalized foods, enabling custom-made dishes tailored to the specific needs of each individual, such as people with allergies or dietary restrictions.
On the sustainability side, researchers are developing 3D printing technologies based on plant proteins or edible powders made from food waste, thus contributing to the reduction of food waste.
Finally, some projects aim to integrate 3D food printing into homes or schools to provide practical and educational solutions around food, while making cooking accessible and creative for everyone.
What are the challenges and limitations of 3D food printing?
3D food printing involves certain challenges and limitations, particularly related to the costs of this technology, the quality of 3D printed products, and food safety.
The Cost of Technology for 3D Food Printing
The technology enabling 3D food printing generally has a high cost, which can vary significantly depending on the types of 3D printers and the materials used.
High-end 3D food printers, especially those intended for professionals or chefs in the gastronomic industry, can cost anywhere from €5,000 to €100,000 due to their precision, advanced features, and the ability to use specific food materials.
More affordable 3D food printers for individuals or small businesses start at prices around €500 to €3,000, but these models may be more limited in terms of material choices and print quality.
In addition to the cost of the 3D food printer, you must also consider the cost of food materials, which can represent a significant budget, with prices varying depending on the type of material and the quantity you want to use.
Quality and Textures of 3D Printed Foods
3D printed foods present a major challenge in terms of quality and texture. Although 3D printing allows exceptional precision in creating shapes and structures, achieving textures identical to those of traditional foods often proves more complex.
The consistency and texture of 3D printed foods depend heavily on the materials used, such as pastas, purees, or gels, which may not offer the same flexibility or elasticity as hand-made foods.
For example, while 3D printed chocolate sculptures or sugar patterns can be highly detailed, their texture may be affected by temperature control or the consistency of the materials. Moreover, complex foods like dishes based on meat or fish are more difficult to print because they require simulating natural textures, such as the grain or fibrousness of muscle fibers.
However, constant progress is being made to improve the quality of 3D printed foods, notably through material innovation and better control of 3D food printer settings.
Food Safety of 3D Printed Foods
The question of food safety is crucial in the field of 3D printed foods. Although 3D printing technology allows the creation of foods with great precision, several factors influence the safety of the finished products.
First, you must ensure that the food materials you use comply with health standards and do not contain harmful or contaminating substances. 3D food printers must also be properly designed and maintained to avoid cross-contamination between different ingredients. This includes rigorous cleaning processes after each use, especially when using different food materials consecutively.
Another major issue is temperature control during printing, particularly for materials like chocolate, dough, or meat-based products. These products can degrade or become a breeding ground for bacterial growth if optimal temperature conditions are not respected.
Furthermore, some experimental projects, such as those using plant proteins or alternative ingredients, require rigorous testing to ensure they are not only edible but also nutritious and safe.
Finally, the traceability of ingredients, their storage, and preparation are also essential to ensure that 3D food printing does not compromise your safety or that of your consumers.
Accessibility and adoption of 3D food printing
3D food printing is limited in its accessibility and inclusiveness due to the cost of equipment and materials, as well as the complexity of this technology. Today, professional 3D food printers remain relatively expensive, making their adoption difficult for small restaurants, pastry chefs, or even individuals.
However, prices are beginning to decrease with the emergence of more affordable consumer models and kits, which tends to encourage broader adoption in the coming years.
Moreover, education and training on how to use this technology play an essential role in its development. The rise of educational programs and workshops to train users in 3D modeling and printer operation helps reduce the barriers that slow down technology adoption.
Furthermore, although the nutritional and creative benefits of 3D food printing exist, large-scale adoption also depends on public acceptance, which requires confidence in the quality and safety of printed foods.
Fortunately, the growing interest in more personalized, sustainable, and innovative food solutions should accelerate the acceptance of this technology, particularly in the fields of gastronomy, education, and industrial food production.
What is the future of 3D food printing?
The future of 3D food printing will certainly involve the evolution of available technologies, the development of its environmental impact, and the market prospects.
Technological Advances in 3D Food Printing
Technological advances in 3D food printing include significant improvements in the precision and speed of printers, enabling more complex and faster creations.
Materials are diversifying with the introduction of plant proteins, algae, and food gels, offering more possibilities for customized dishes.
Advances in temperature control ensure consistent results, and modeling technologies are becoming more accessible, even for non-specialized users.
Finally, progress in food safety and printer cleaning enhances the overall reliability of the technology.
Environmental Impact of 3D Food Printing
The environmental impact of 3D food printing is both positive and negative. This technology helps reduce food waste by printing precise portions and using sustainable ingredients such as plant proteins, algae, or insects.
However, the use of materials and the energy required to operate the printers can increase the ecological footprint. Additionally, printing generates non-food plastic waste, which limits its environmental benefits.
Trends and Market Prospects of 3D Food Printing
3D food printing is experiencing rapid growth, with promising market prospects. This technology is increasingly used in the gastronomy industry, high-end restaurants, and personalized food services. The demand for custom meals and alternative ingredients, such as plant proteins, is driving its adoption.
Technological advances and the reduction in printer costs also help broaden access for small businesses and individuals.
In the long term, 3D food printing could transform food production by reducing waste, optimizing nutrition, and facilitating sustainable food solutions. The market is expected to continue growing with increased interest in personalization, innovation, and sustainability.
Conclusion : 3D food printing
In conclusion, 3D food printing represents a major advance in the culinary sector, offering infinite possibilities in terms of creation, personalization, and sustainability. Although 3D food printing still faces significant challenges, notably regarding costs, material quality, and food safety, this technology opens promising prospects for the future of food.
From the production of personalized meals to the reduction of food waste, 3D printing has the potential to transform the industry by meeting the needs of a more responsible and innovative consumption.
Image generated by DALL·E, an artificial intelligence model developed by OpenAI.
The articles published on Imprimy.com are for informational purposes only. They are intended to provide general advice and information related to 3D printing. Imprimy.com cannot be held responsible for the results obtained or the consequences arising from the application of the shared information. We recommend always checking the specific instructions for your hardware and materials before use.