Are you interested in articulated 3D prints and want to know how they are made to be durable in use? Imprimy is here to provide all the answers to your questions.
Articulated 3D printing is an innovative technique that enables the fabrication of mobile objects and complex assemblies in a single step through precise modeling that integrates functional articulated mechanisms without the need for manual assembly.
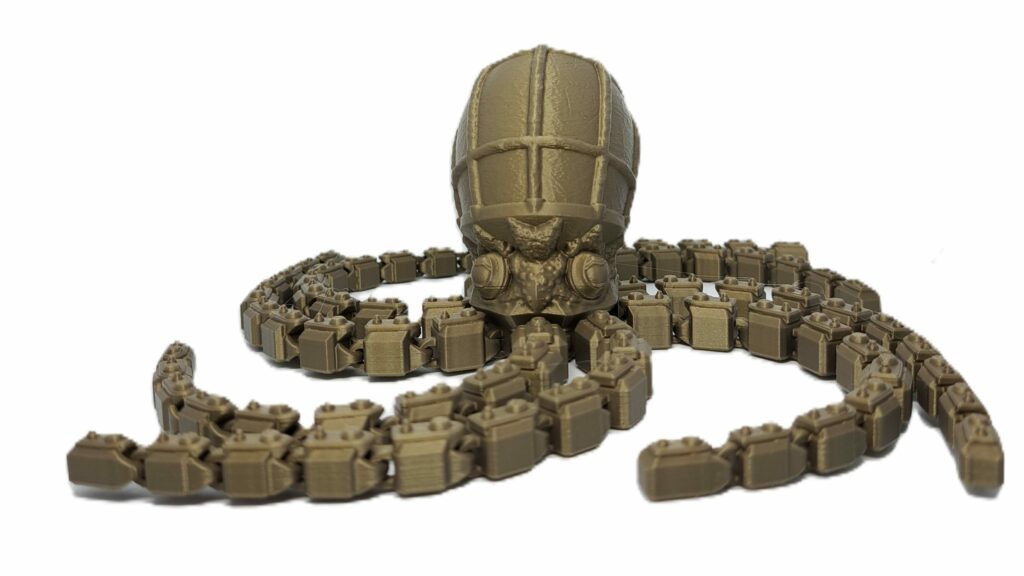

What is articulated 3D printing?
Articulated 3D printing is an additive manufacturing method that allows the creation of mobile objects made up of articulated parts integrated directly during printing, without requiring post-print assembly.
The definition of articulated 3D printing
Articulated 3D printing refers to an additive manufacturing technique that enables the production of objects composed of moving parts, such as hinges, bearings, or axes, in a single print without the need for manual assembly afterward.
This is made possible thanks to a specific modeling approach that includes clearance spaces between elements to ensure smooth and functional articulation.
The differences with traditional 3D printing
Unlike traditional 3D printing, which typically produces fixed parts that must be manually assembled to create moving components, articulated 3D printing directly integrates mobile mechanisms into the digital model, allowing the creation of complete assemblies in a single step with controlled clearances to ensure mobility.
This type of 3D printing thus requires more complex modeling, higher printing precision, and specific management of spacing, making it more technical but significantly more practical for producing functional objects ready to use.
What are the advantages of articulated 3D printing?
Articulated 3D prints offer major advantages such as the creation of mobile objects without assembly, high customization, reduced manufacturing times, flexibility in complex designs, and the ability to produce functional prototypes ready for use, all while fostering innovation and creativity.
The flexibility and adaptability of articulated 3D prints
Articulated 3D printing offers exceptional flexibility and adaptability by enabling the creation of customized mechanisms and complex shapes perfectly tailored to the specific needs of each project.
It allows you to design modular objects, adjustable prototypes, or realistic biomechanical models, while facilitating quick modifications and custom adjustments, making it an ideal solution for innovation, research, and the production of unique parts or limited series.
Practical applications of articulated 3D printing
Articulated 3D prints have diverse practical applications, including the creation of :
- articulated toys,
- mobile figurines,
- biomechanical prosthetics,
- robots,
- functional models for engineering or architecture.
They are also used to produce dynamic prototypes, test complex mechanisms before mass production, create modular tools, and develop custom replacement parts.
Innovations and creativity in articulated 3D printing
Articulated 3D printing stimulates innovation and creativity by enabling the design of unprecedented shapes, complex mechanisms, and interactive objects that are impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
This specific 3D printing opens the door to original designs, artistic projects, futuristic prototypes, and custom solutions, encouraging creators, engineers, and makers to experiment with novel concepts, push the boundaries of personalization, and explore new possibilities for smart and functional products.
What materials are used for articulated 3D prints?
Articulated 3D prints primarily use materials such as PLA, ABS, and PETG, as well as flexible filaments like TPU, and sometimes special resins or composites to ensure a combination of strength, flexibility, and durability for the moving parts.
The different types of materials used for articulated 3D printing
Articulated 3D prints use a wide variety of materials suited for creating moving parts, including PLA, which is easy to print and ideal for simple prototypes; ABS, which is more resistant and flexible; PETG, valued for its strength and durability; and technical filaments like TPU for flexible joints and elastic elements. Some projects also incorporate special resins for extreme fineness or metals and composites for robust and functional parts, offering a broad selection depending on mechanical constraints and the final use.
Durability and recycling of articulated 3D prints
The durability of articulated 3D prints depends on the choice of materials, the quality of the print, and the maintenance of mechanisms, with filaments like PETG or ABS offering better resistance and longer lifespan for heavily used joints.
On the recycling side, an increasing number of biodegradable filaments such as PLA and recycled materials help reduce environmental impact, alongside initiatives to reuse scraps and reprint damaged parts, contributing to a more ecological and responsible approach to articulated 3D printing.
What are the limitations of articulated 3D printing?
The limitations of articulated 3D printing include the high precision required to prevent sticking of moving parts, the fragility of fine joints, constraints related to available materials, the complexity of design, as well as size restrictions and higher costs compared to traditional 3D printing.
The technical complexity of articulated 3D printing
Articulated 3D printing presents a higher technical complexity than classic 3D printing because it requires precise modeling of the clearance spaces between moving parts to prevent them from fusing during printing, fine calibration of the printer to ensure dimensional accuracy, and strong mastery of printing parameters such as temperature, speed, and infill.
It also demands a deep understanding of the mechanical constraints of materials and anticipation of friction points, making expertise in 3D design essential to achieve functional and durable joints.
The cost of an articulated 3D print
ChatGPT a dit :
The cost of an articulated 3D print is generally higher than classic 3D printing due to the complexity of modeling, longer printing times required for detailed mechanisms, and the possible need for more expensive specialized materials.
Additionally, factors such as printer maintenance, prototype testing to adjust clearance spaces, and skilled labor for proper design and setup must be considered, making articulated 3D printing a more technical but cost-effective solution for functional, customized, and ready-to-use objects.
Current limitations of articulated 3D printing
The current limitations of articulated 3D printing mainly lie in the precision required to prevent the sticking of moving parts during printing, the relative fragility of fine joints under high mechanical stress, and the size restrictions imposed by printer technology.
Additionally, the complexity of design demands advanced skills, and some suitable materials remain expensive or limited in availability, which still hinders mass production and large-scale distribution, although ongoing technical advancements continue to improve these aspects.
Conclusion: Articulated 3D Printing
Articulated 3D printing represents a technological revolution that transforms additive manufacturing by enabling the creation of mobile and functional objects in a single step, thus opening up unprecedented opportunities in design, customization, and innovation.
Despite its technical constraints, costs, and current limitations, this technology continues to advance rapidly, offering increasingly flexible, durable, and adapted solutions for a wide range of applications, from industry to craftsmanship, while fostering creativity and the exploration of new interactive forms.
Photo : Imprimy.com / Model : Props & Beyond.
The articles published on Imprimy.com are for informational purposes only. They are intended to provide general advice and information related to 3D printing. Imprimy.com cannot be held responsible for the results obtained or the consequences arising from the application of the shared information. We recommend always checking the specific instructions for your hardware and materials before use.