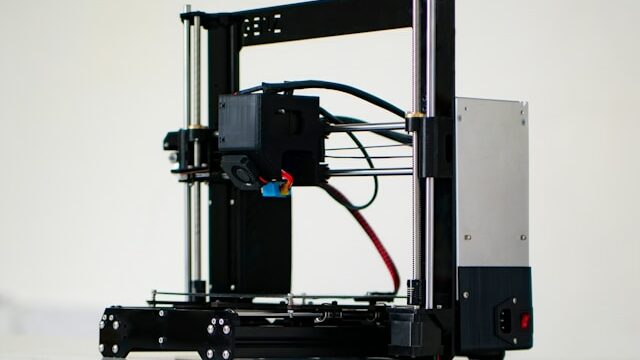
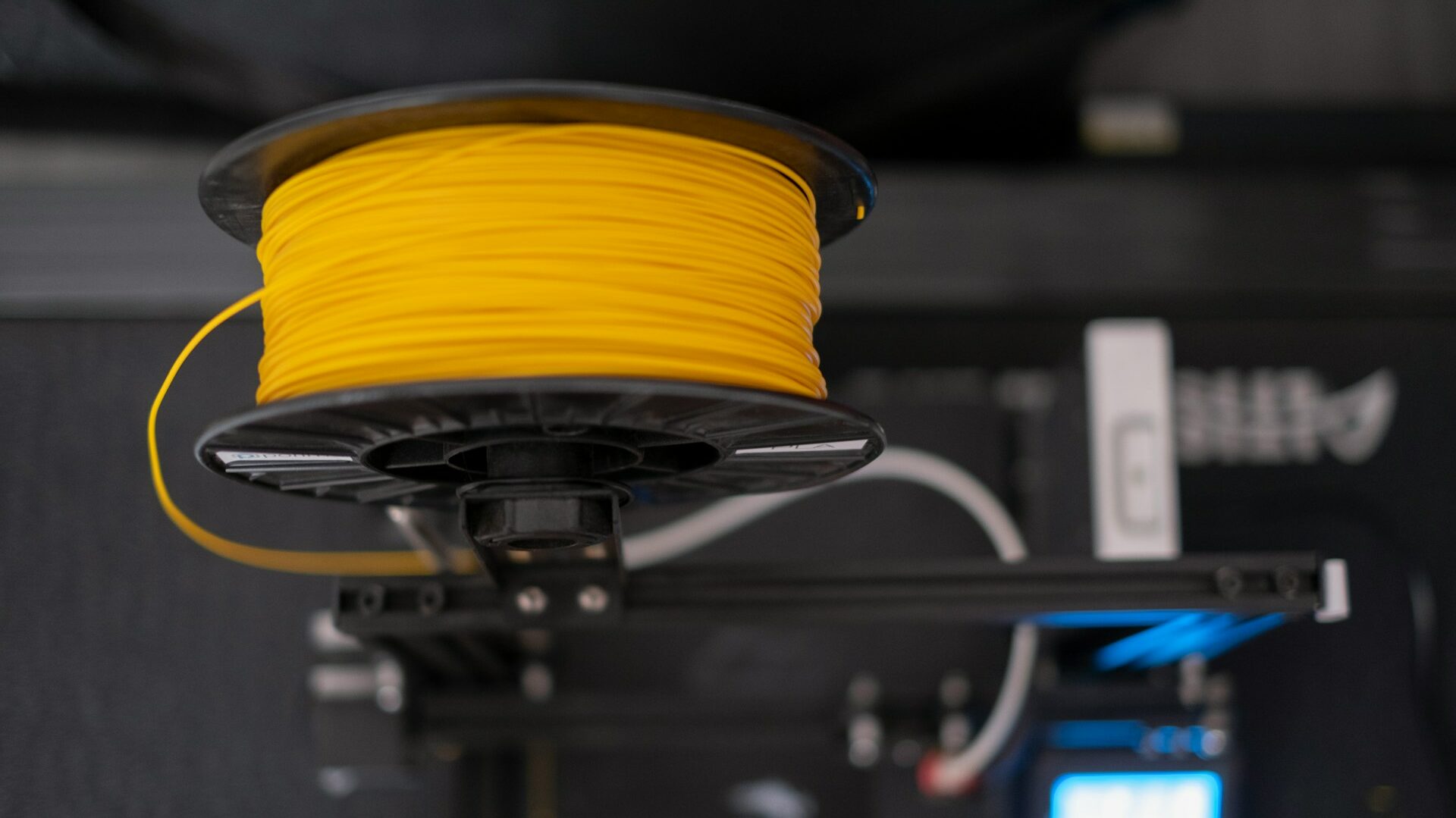
Do you want to discover everything you need to know about FDM 3D printing? At Imprimy, we are here to explain everything about this type of 3D printers.
FDM 3D printing is an accessible, versatile, and cost-effective technology that creates objects by depositing, layer by layer, a melted thermoplastic filament.
What is FDM 3D Printing?
FDM 3D printers are specialized printers that use thermoplastic filaments to create three-dimensional objects.
How FDM Printing Works
FDM 3D printing (Fused Deposition Modeling) works by extruding melted thermoplastic filament, deposited layer by layer. The filament is heated in a moving nozzle that traces the model according to a digital file.
Each layer solidifies as it cools down, gradually forming the final object. This process is valued for its simplicity, affordable cost, and versatility.
The materials used for FDM printing
The main materials used in FDM printing are thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and PETG. PLA is easy to print and biodegradable, ideal for beginners.
ABS is more durable but requires a heated enclosure. PETG combines strength, flexibility, and ease of printing.
The components of an FDM printer
An FDM printer mainly consists of an extruder, which pushes the filament, and a heated nozzle, which melts it. The print bed, often heated, receives the layers of material.
Motors move the nozzle and the bed along the X, Y, and Z axes. A motherboard controls everything through integrated software.
What are the advantages of FDM 3D printing?
FDM 3D printing’s main advantages are that it is accessible, versatile, and also easy to use.
The accessibility and cost of FDM 3D printing
FDM 3D printing is the most accessible technology on the market. Printers are available starting at just a few hundred euros, with a low filament cost.
It is perfectly suited for individuals, makers, and small businesses. Its quality/price ratio makes it a popular solution for prototyping and custom object creation.
The versatility of the different compatible materials
The materials compatible with FDM printing offer great versatility depending on the needs. PLA is ideal for prototypes, ABS for technical parts, and PETG for moisture-resistant objects.
Special materials like TPU (flexible) or fiber-filled filaments (carbon, wood) expand the possibilities. This diversity allows adapting printing to various uses: educational, industrial, artistic, or domestic.
The ease of use of FDM printers
FDM printers are known for their ease of use, even for beginners. Installation, filament loading, and starting a print are usually done in just a few steps.
Many models offer intuitive interfaces and automatic assistance (calibration, leveling). This makes it an ideal solution for quick learning of 3D printing.
What are the different applications of FDM 3D printing?
FDM 3D printing enables many applications such as rapid prototyping, in education, industrial applications, and even creative uses.
Rapid prototyping
FDM 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, transforming an idea into a physical object in just a few hours. It facilitates frequent iterations at low cost, ideal for testing concepts.
Companies gain flexibility and development time. It is a key tool for innovation and agile design.
Education and Training
FDM printing is widely used in education to introduce students to digital technologies and 3D design. It allows for hands-on and engaging learning in fields like science, technology, and art.
Its affordable cost and ease of use make it an ideal tool for schools. It fosters creativity, problem-solving, and technical skills.
Industry and Industrial Markets
FDM 3D printing finds its place in industry for prototyping, manufacturing jigs, functional parts, or small batches. It reduces production time and costs while offering great flexibility.
Sectors like automotive, aeronautics, and electronics use it to accelerate product development. It is a key technology for industry.
Domestic and Creative Uses
FDM 3D printing allows you to create useful or customized objects at home: tools, storage, spare parts. It also opens the way to creative projects like decorative items, accessories, or custom toys.
Online platforms offer thousands of ready-to-print models. Accessible and fun, it stimulates creativity every day.
What tips should be followed to get started with FDM printing?
To get started with FDM 3D printing, you should ensure you choose the right machine, prepare your model properly, and optimize it while avoiding common mistakes.
Choosing the right FDM 3D printer
To choose an FDM 3D printer, you need to consider the print resolution, the build volume size, and the reliability. The user’s experience level also influences the choice: ready-to-use models for beginners or modular machines for experts.
The budget remains a key criterion, as well as the availability of consumables and technical support. Comparing these aspects helps find the printer suited to your needs.
Properly preparing your model for 3D printing
To properly prepare your model for FDM 3D printing, start by checking its integrity and closure in a modeling software. Then, use a slicer to generate the G-code file, adjusting parameters like infill density, print speed, and temperature.
Remember to add support structures if necessary for overhanging parts. Good preparation ensures a precise and flawless print.
Optimizing your 3D print settings
To optimize your FDM 3D prints, adjust the nozzle and bed temperature according to the filament used. Set the print speed for a good balance between quality and speed.
Remember to calibrate bed leveling and retraction to avoid defects like stringing or warping. Testing different parameters helps achieve precise and durable results.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in 3D Printing
To avoid common errors in FDM 3D printing, make sure to have good bed leveling before each print. Avoid too high temperatures that cause blobs or warping.
Also, check the filament quality to prevent extruder jams. Finally, plan supports for overhanging parts to avoid structural defects.
What are the innovations associated with FDM printing?
FDM 3D printing has seen several innovations over the years that have enhanced its capabilities, accuracy, and overall user experience.
Technological Advances in FDM Printers
FDM printers benefit from advancements like dual extruders for multi-material or multi-color printing. Automatic sensors improve bed leveling and filament end detection.
The integration of artificial intelligence optimizes parameters in real time. These innovations make printing more precise, fast, and accessible.
The Evolution of Industrial Applications of FDM Printing
The evolution of industrial applications of FDM printing is reflected in increasing use for the manufacturing of functional parts and complex prototypes. Industries now utilize advanced materials offering greater strength and durability.
Integration into additive manufacturing enables custom small batches and significant time savings. This technology is becoming a key driver of industry and custom manufacturing.
The Use of Increasingly Eco-Friendly Materials in FDM Printing
FDM 3D printing is evolving towards increasingly eco-friendly materials, such as bio-based and biodegradable PLA. New filaments incorporate natural additives (wood, plant fibers) to reduce the environmental impact.
Recycling filaments and using recycled plastics are gaining popularity. These innovations support a more sustainable and responsible 3D printing.
Conclusion: FDM 3D Printing
FDM 3D printing is an accessible, versatile, and cost-effective technology, ideal for prototyping, artistic creation, and industrial uses. Its ease of use and the variety of compatible materials make it an essential tool.
Technological advancements and the shift towards more eco-friendly materials strengthen its potential. FDM continues to transform the way we design and manufacture objects.
Picture by Osman Talha Dikyar on Unsplash.
The articles published on Imprimy.com are for informational purposes only. They are intended to provide general advice and information related to 3D printing. Imprimy.com cannot be held responsible for the results obtained or the consequences arising from the application of the shared information. We recommend always checking the specific instructions for your hardware and materials before use.