Do you want answers to all your questions about 3D print warping? At Imprimy.com, we’re here to help you.
To prevent warping in 3D printing, carefully control printing temperatures, maintain a clean and heated print surface, optimize model design and manage the printing environment.

What is 3D print warping?
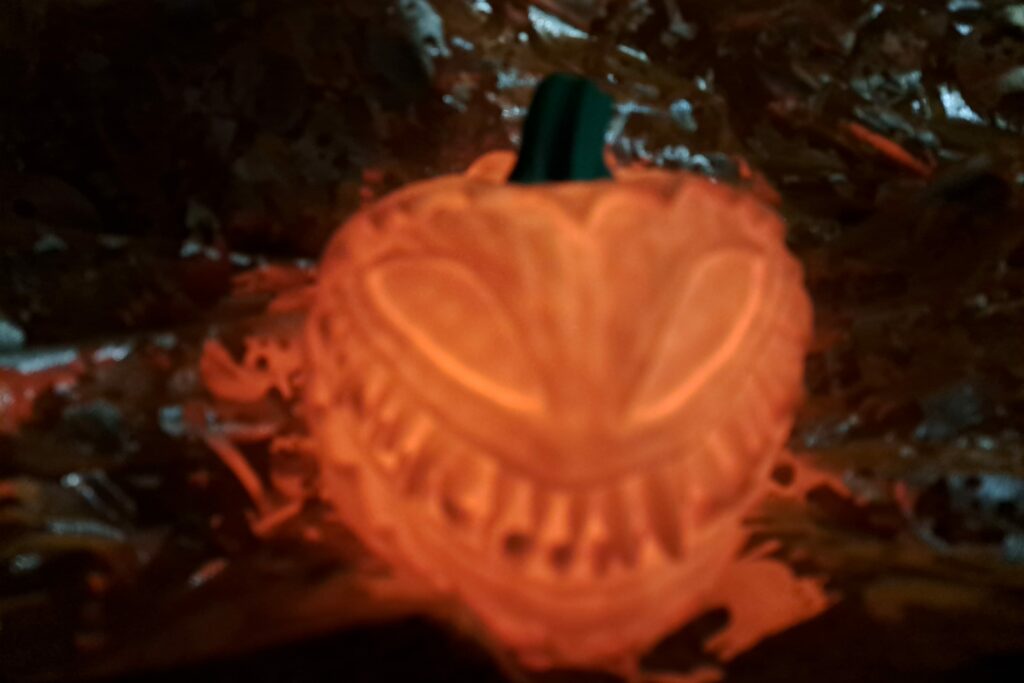
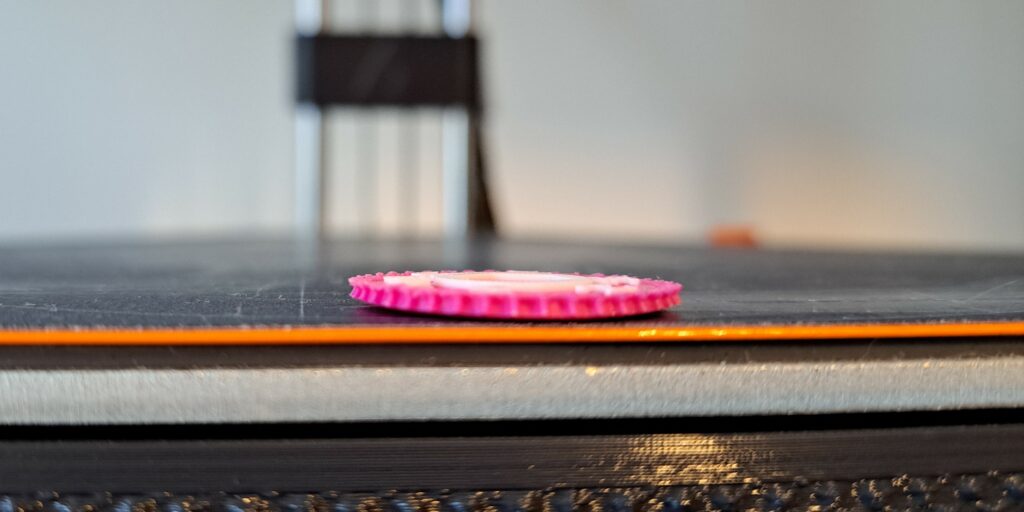
3D print warping is the distortion that occurs when printed material cools unevenly, causing edges or corners to lift and deform.
Definition of warping
Warping in 3D printing is the distortion that occurs when printed layers cool unevenly, causing edges or corners to lift from the print bed. This happens because the material contracts as it solidifies, creating internal stresses.
Warping is especially common with certain plastics like ABS. It can lead to deformed or unusable parts if not properly managed.
The different symptoms of warping
The main symptoms of warping include lifting or curling of the print’s corners and edges during or after printing. You may also notice the base of the print becoming uneven or unstable.
In severe cases, the print can partially or completely detach from the build plate. These issues are more common with large prints or certain materials prone to shrinkage.
What are the main causes of warping in 3D printing?
The main causes of warping in 3D printing are uneven cooling, poor bed adhesion, incorrect temperature settings, and unsuitable model design.
The temperature of the print surface
The temperature of the print surface is crucial in preventing warping. A heated bed helps keep the first layers warm, improving adhesion and reducing rapid cooling.
Different materials require specific bed temperatures, such as around 60°C for PLA and 100°C for ABS. Maintaining the right surface temperature ensures the print sticks properly throughout the process.
The temperature of the nozzle
Nozzle temperature plays a vital role in ensuring proper layer bonding and reducing warping. If the temperature is too low, layers may not fuse well, causing weak spots and lifting.
Conversely, too high a temperature can cause excessive melting or stringing. Setting the nozzle within the recommended range for the filament type ensures strong, consistent extrusion and minimizes deformation.
The issue of material retraction
Material retraction refers to the shrinkage that occurs as the filament cools and solidifies, creating internal tension. This tension can cause corners or edges of the print to lift, leading to warping.
Materials like ABS and nylon are particularly prone to this issue. Managing cooling rates and using enclosures can help reduce retraction effects.
The design and geometry of the model
The design and geometry of a 3D model greatly influence its risk of warping. Large flat surfaces, sharp corners, and uneven thicknesses increase internal stress during cooling.
To reduce warping, designers can use rounded edges, minimize surface contact, and add features like brims or rafts. Smart design choices help distribute heat more evenly and improve bed adhesion.
Cleaning the print surface
A clean print surface is essential for proper filament adhesion and warping prevention. Dust, oil, or leftover residue can reduce grip, causing the print to lift.
Regularly cleaning the bed with isopropyl alcohol or mild soap ensures optimal contact. A well-maintained surface leads to more reliable and successful prints.
What are the effects of warping on 3D prints?
Warping causes dimensional inaccuracies, surface defects, layer separation, and can lead to print failure or unusable parts.
The impact of warping on the quality of your parts
Warping negatively affects the dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and appearance of 3D printed parts. It can cause uneven bases, misaligned layers or cracks in the print.
In severe cases, the part may become completely unusable. Preventing warping is key to achieving high-quality, functional prints.
The consequences on cost and printing time
Warping increases both the cost and time of 3D printing by causing failed prints and wasted materials. Reprinting parts consumes additional filament, energy, and labor.
It also delays project timelines, especially in batch or large-scale productions.Preventing warping helps reduce waste and improve overall printing efficiency.
How to prevent and correct warping during the 3D printing process?
To prevent and correct warping, optimize bed and nozzle temperatures, ensure a clean and heated print surface, use adhesives or specialized build plates, control the printing environment, and adjust model design and slicing settings.
Optimizing the printing temperature
Optimizing printing temperature involves setting the nozzle and bed to the ideal range for the specific filament used. This ensures proper layer adhesion and reduces the risk of thermal stress and warping.
Too low a temperature can cause poor bonding, while too high can lead to overheating issues. Fine-tuning these settings improves print quality and stability.
The use of print surfaces and adhesives
Using specialized print surfaces like PEI sheets, glass beds or BuildTak can significantly enhance adhesion and reduce warping. Adhesives such as glue sticks, hairspray or tape further help the first layers stay firmly in place.
These tools create a strong bond between the print and the bed, minimizing edge lifting. Choosing the right surface and adhesive is key to successful, warp-free prints.
Improving the model design
Improving model design can significantly reduce warping by minimizing large flat surfaces, adding rounded corners and maintaining consistent wall thickness.
Features like brims or rafts can also be added to enhance bed adhesion. Redesigning parts with warping in mind helps distribute stress more evenly during cooling. Smart design choices lead to more stable and reliable prints.
Controlling the printing environment
Controlling the printing environment helps maintain consistent temperatures and prevents drafts that can cause uneven cooling and warping. Using an enclosed printer or adding a chamber keeps heat around the print, reducing thermal stress.
Avoiding sudden changes in room temperature is also important. A stable environment leads to better adhesion and overall print quality.
What are the tools and accessories to fight warping?
Tools and accessories to fight warping include heated beds, adhesive sprays or tapes, specialized print surfaces like PEI sheets, and enclosed printer chambers to maintain stable temperatures.
3D printers with heated beds
3D printers with heated beds are essential for reducing warping, especially when printing with materials like ABS or PETG. The heated surface keeps the bottom layers warm, preventing rapid cooling and shrinkage.
This improves first-layer adhesion and reduces the chances of corners lifting. Heated beds are a key feature for consistent, high-quality prints.
The use of special materials and coatings
Special materials like PLA are less prone to warping, while ABS or nylon require more careful handling. Applying coatings such as glue sticks, hairspray, or Kapton tape enhances bed adhesion and reduces edge lifting.
These treatments create a better surface for the filament to stick to during printing. Choosing the right material and coating is crucial to prevent warping effectively.
Slicing software and printing settings
Slicing software allows precise control over printing settings that impact warping, such as temperature, speed, and layer height. It also enables adding brims, rafts, or supports to improve bed adhesion and stability.
Properly configured settings help minimize thermal stress and prevent deformation. Using the right slicer settings is key to successful, warp-free prints.
Conclusion: 3D Print Warping
Warping is a common challenge in 3D printing that can compromise print quality and usability. By controlling temperatures, optimizing design, preparing the print surface, and managing the environment, warping can be effectively minimized.
Combining these strategies ensures stronger adhesion and reduces internal stresses. Mastering warping prevention leads to more reliable and precise 3D prints.
Photo by Imprimy.com
The articles published on Imprimy.com are for informational purposes only. They are intended to provide general advice and information related to 3D printing. Imprimy.com cannot be held responsible for the results obtained or the consequences arising from the application of the shared information. We recommend always checking the specific instructions for your hardware and materials before use.