Do you want to print or order a 3D printed vase but don’t know what that involves? At Imprimy.com, we’re here to answer all your questions on this topic.
You can create a unique vase using 3D printing technology to personalize your home decor.
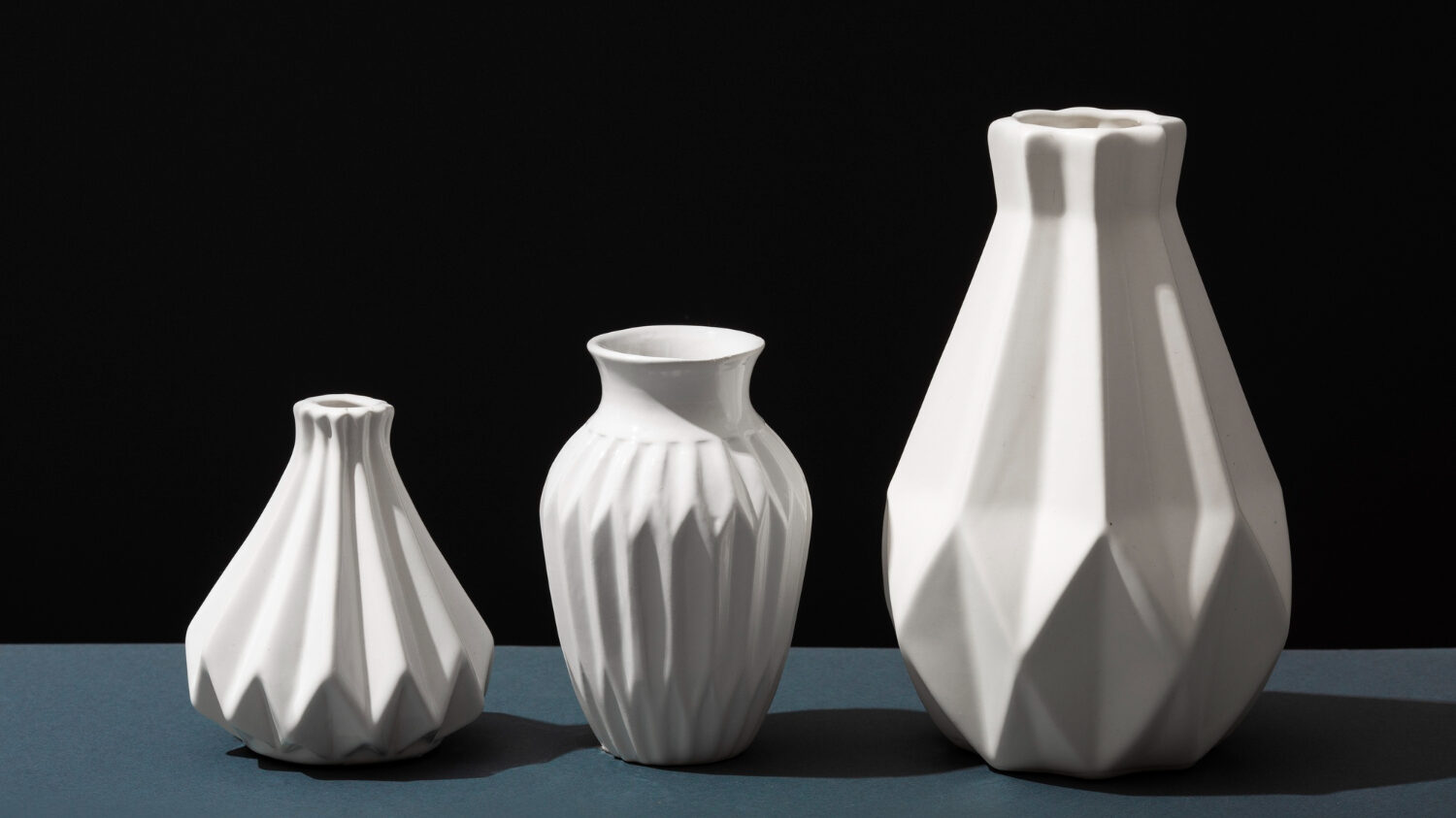

Why Choose a 3D Printed Vase?
Choose a 3D printed vase for its endless customization and fast production, tailored to your specific tastes.
Customization of a 3D Printed Vase
Customization of a 3D Printed Vase allows for the creation of unique and tailor-made objects. Thanks to this technology, designers can model complex and original shapes, adapted to individual preferences.
3D printing offers great flexibility in choosing materials and colors, making it possible to create vases that perfectly fit into home decor.
Moreover, this manufacturing method is often more economical and eco-friendly than traditional techniques, as it reduces material waste. 3D printing customization thus opens up new creative and functional possibilities in the field of interior decoration.
The Durability of a 3D Printed Vase
The durability of a 3D printed vase depends on several key factors. The choice of material is crucial: plastics like PLA or ABS are commonly used, but eco-friendly options, such as biodegradable PLA or plant-based resins, are gaining popularity. The quality of the print and the vase design also influence its longevity. A well-designed vase, with a solid structure and thicker walls, will better resist daily wear and tear.
Additionally, 3D printing allows for local and on-demand production, reducing transport emissions and material waste. Finally, proper maintenance and careful use help extend the vase’s lifespan, making 3D printing a potentially sustainable option for vase creation.
Savings Achieved with 3D Printed Vases
The savings from 3D printed vases come from several key advantages of this technology.
First, 3D printing enables on-demand production, eliminating storage costs and overproduction.
Additionally, it reduces material waste, as only the necessary amount is used — unlike traditional manufacturing methods. Transportation costs are also lowered thanks to the ability to produce locally.
Moreover, 3D printing offers design flexibility, allowing the creation of custom vases without the high costs associated with mold or tooling modifications.
Finally, using more affordable materials and optimized production processes further reduces overall costs, making 3D printed vases an economically advantageous choice.
What Are the Best Materials for 3D Printing Vases?
The best materials for 3D printing vases are PLA for its ease of use, PETG for its durability, and resin for fine details.
The Different Types of Materials for 3D Printing, Their Advantages and Disadvantages
The materials used to create a 3D printed vase each have their own advantages and disadvantages:
- Metals like steel and aluminum are strong and durable, but they can be heavy and expensive.
- Plastics offer lightness and versatility, but their environmental impact is often negative due to their low biodegradability.
- Composite materials combine strength and lightness, but their cost can be high, and recycling them can be complex.
- Ceramics are heat and corrosion resistant, but they can be fragile and difficult to machine.
- Natural materials like wood are aesthetic and renewable, but they may require regular maintenance and can be sensitive to the weather.
- Biomaterials and recycled materials help reduce carbon footprints, but they may have performance limitations and can be less readily available.
Each material should therefore be chosen based on the specific needs and constraints of the project.
Choosing the Material for 3D Printing a Vase
The choice of material for 3D printing a vase is crucial and depends on several factors. Plastics are commonly used due to their accessibility and ease of printing, with PLA being biodegradable. For more durable and resistant vases, resins can be an option, although they often require post-processing.
Composite materials and ceramics offer a unique aesthetic and increased strength, but they can be more expensive and complex to print. Biomaterials and recycled materials are becoming increasingly popular due to their reduced environmental impact, although their mechanical properties can vary.
The final choice will depend on specific requirements in terms of design, functionality, budget, and durability.
What are the Steps to Create a 3D Printed Vase?
The steps to create a 3D printed vase include 3D model design, digital slicing, layer-by-layer printing, and post-processing for a perfect finish.
Designing a 3D Printed Vase
The design of a 3D printed vase involves several key steps to ensure both aesthetic appeal and functionality. The process begins with 3D modeling of the vase, typically done using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This stage allows you to define the shape, size, and intricate details of the vase. It’s crucial to consider specific constraints related to 3D printing, such as wall thickness and overhang angles, to ensure successful printing.
Once the model is finalized, it is converted into an STL file, which is then prepared for printing using slicing software. This software determines the print parameters, such as resolution and infill density, which affect the strength and quality of the vase. By considering these steps, you can create a well-designed 3D printed vase that is both visually appealing and functional.
Preparing the 3D Print of Your Vase
The preparation for 3D printing a vase is a crucial step to ensure a successful print. Once the 3D model is designed, it is exported in STL format, a standard format for 3D printing. This file is then imported into slicing software, which converts the model into instructions that the 3D printer can follow.
Slicing involves setting key parameters, such as:
- Layer height, which affects the resolution and surface quality of the vase. A smaller layer height results in a smoother finish but requires more time.
- Infill density, which determines the object’s strength and weight. Higher infill makes the vase more durable but also heavier, while lower infill reduces material usage and weight.
- Support structures: If your vase has overhangs or complex features, you’ll need to set up supports to ensure these parts print properly.
- Printing temperature: The printing temperature should be set according to the material being used. For example, PLA typically requires a lower temperature than ABS or PETG.
- Positioning the model on the print bed is crucial to prevent warping and ensure good adhesion. If necessary, you can also add additional support structures to prevent deformation during printing.
By carefully preparing these parameters, you can optimize the printing process and minimize errors, resulting in a high-quality 3D printed vase.
3D Printing the Vase
3D printing a vase is the process where the prepared digital model is transformed into a physical object. Once the STL file is sliced and the print settings are configured, the 3D printer deposits material layer by layer onto the print bed.
The print accuracy depends on the chosen resolution, with finer layers resulting in a smoother surface finish. During the printing process, it’s essential to monitor for potential issues such as warping or detachment from the print bed. Ensuring proper adhesion during the first layers and watching for any inconsistencies helps ensure the vase prints successfully.
This layer-by-layer method allows for intricate designs and can create vases with complex shapes and detailed textures.
Post-Processing of Your 3D Printed Vase
Post-processing a 3D printed vase is an important step to enhance both its appearance and functionality. After printing, the vase may require the removal of supports, which are temporary structures added to support overhanging parts during the print. This can be done manually or with specific tools designed for support removal.
Next, sanding the surface helps to smooth out any imperfections and improve the texture. For a more professional finish, painting or varnishing can be applied, offering additional protection and a more refined look. In some cases, advanced techniques such as chemical polishing or heat treatment may be used to improve the vase’s strength and durability.
These post-processing steps transform the 3D printed vase into an aesthetically pleasing and functional object, ready for use or display.
What advice should be applied to succeed in your 3D printing?
To succeed in your 3D printing, follow these tips: calibrate your printer, use settings suited to the material, ensure good adhesion of the first layer, and clean your machine regularly.
Your 3D printing settings to create a vase
The 3D printing settings to create a vase must be carefully chosen to ensure high-quality prints. Here are some key parameters to consider:
- Layer height: A finer layer height (for example, 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm) improves resolution and surface quality of the vase, though this may increase print time.
- Infill density: A denser infill (for example, 20% to 50%) will make the vase stronger and more durable, but it will also increase weight and material consumption.
- Printing temperature: The temperature should be adjusted based on the material used. For example, PLA is typically printed between 190°C and 220°C, while ABS requires higher temperatures.
- Print speed: A slower speed can improve precision and print quality, while a faster speed reduces print time but may affect finish quality.
- Printing supports: If the vase design has overhangs, supports may be needed to prevent deformation. These supports should be configured in the slicing software.
- Bed adhesion: Using a skirt or brim can improve the first layer adhesion to the print bed, reducing the risk of detachment.
- Bed temperature: An appropriate bed temperature (for example, 60°C for PLA) helps prevent warping and improves adhesion.
These parameters should be adjusted according to the specific design of the vase and the chosen material to achieve the best possible results.
Resolving common issues related to 3D printing
Resolving common issues related to 3D printing is essential for ensuring successful prints. Here are some frequent problems and their solutions:
- Bed detachment: This problem can be resolved by improving the adhesion of the first layer. Using a skirt or brim, increasing the bed temperature, or applying a specific adhesive can help.
- Warping and shrinkage: Deformations can be reduced by adjusting the printing temperature and using a heated enclosure to maintain a constant temperature around the print.
- Material stringing: Stringing can be minimized by adjusting retraction settings in the slicing software, lowering the printing temperature, or increasing travel speed.
- Over-extrusion or under-extrusion: These issues can be corrected by calibrating the extrusion flow rate and ensuring that the filament is properly fed without obstructions.
- Difficult support removal: Using soluble supports or optimizing support settings in the slicing software can make them easier to remove.
- Visible layer lines: Reducing the layer height and adjusting the print speed can improve surface quality and reduce the visibility of layers.
- Clogged nozzle: Regularly cleaning the nozzle and using high-quality filament can prevent clogs. In case of a clog, a hot cleaning process may be necessary.
By identifying and correcting these problems, it is possible to improve the quality and reliability of 3D printing.
Maintenance of the 3D printer used for printing a vase
La maintenance d’une imprimante 3D est cruciale pour garantir des impressions de qualité et prolonger la durée de vie de l’équipement. Voici quelques pratiques Maintenance of a 3D printer is crucial to ensure quality prints and extend the equipment’s lifespan. Here are some essential practices:
- Regular cleaning: Clean the print bed and nozzle regularly to prevent material residue buildup that could affect print quality.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the rails and gears to ensure smooth movement of moving components and reduce wear.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the bed and extruder to ensure the printer operates optimally.
- Belt inspection: Check the belts for signs of wear or looseness, and replace them if necessary.
- Firmware updates: Keep the firmware up to date to benefit from the latest improvements and bug fixes.
- Proper filament storage: Store filament in a dry environment, protected from light, to prevent moisture absorption, which can cause printing issues.
- Inspection of electronic components: Check the electrical connections and components to ensure they are in good condition and securely fastened.
By following these maintenance practices, you can minimize printer failures and printing issues while extending the lifespan of your 3D printer.
Conclusion: 3D Printed Vase
Printing a vase with a 3D printer offers endless creative possibilities and customization. By carefully selecting the right settings, such as layer height, infill density, and printing temperature, as well as ensuring proper maintenance and regular calibration, you can achieve high-quality results. Addressing common issues like bed detachment and stringing will further improve the print’s success rate.
The 3D printing process allows for intricate designs and personal expression, and with proper attention to detail, your vase can turn out both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Regular maintenance of the printer will ensure reliable performance over time, making it a valuable tool for creating unique and beautiful pieces.
Picture by Freepik.
The articles published on Imprimy.com are for informational purposes only. They are intended to provide general advice and information related to 3D printing. Imprimy.com cannot be held responsible for the results obtained or the consequences arising from the application of the shared information. We recommend always checking the specific instructions for your hardware and materials before use.